Just like a car needs fuel to operate, the human body requires energy to function properly—and that energy comes from food. In simple terms, food contains compounds that our bodies convert into other compounds, releasing energy in the process. This type of conversion, or chemical reaction, is called exothermic, meaning it releases energy as heat. Without this heat, our bodies would become too cold to carry out the necessary chemical and biological functions needed for survival. At the same time, the body maintains its temperature and regulates energy production through a process called homeostasis, ensuring that cells get the right amount of fuel without overheating. The body’s main source of energy are carbohydrates.
Carbohydrates are divided into two groups: simple and complex carbohydrates. The main difference between them lies in their chemical structure, which affects how quickly the body can extract energy from them. Simple carbohydrates provide quick energy because they are already in a form the body can easily use. In contrast, complex carbohydrates need to be broken down into simpler forms before the body can extract energy, which results in a slower, more sustained release.
Simple carbohydrates are also known as sugars and are further classified into monosaccharides and disaccharides. These sugars are responsible for the sweet taste of foods like honey and fruit. Complex carbohydrates, on the other hand, include oligosaccharides and polysaccharides, which are made up of longer chains of sugar molecules. Oligosaccharides consist of 3 to 9 sugar units, while polysaccharides are made of 10 or more.
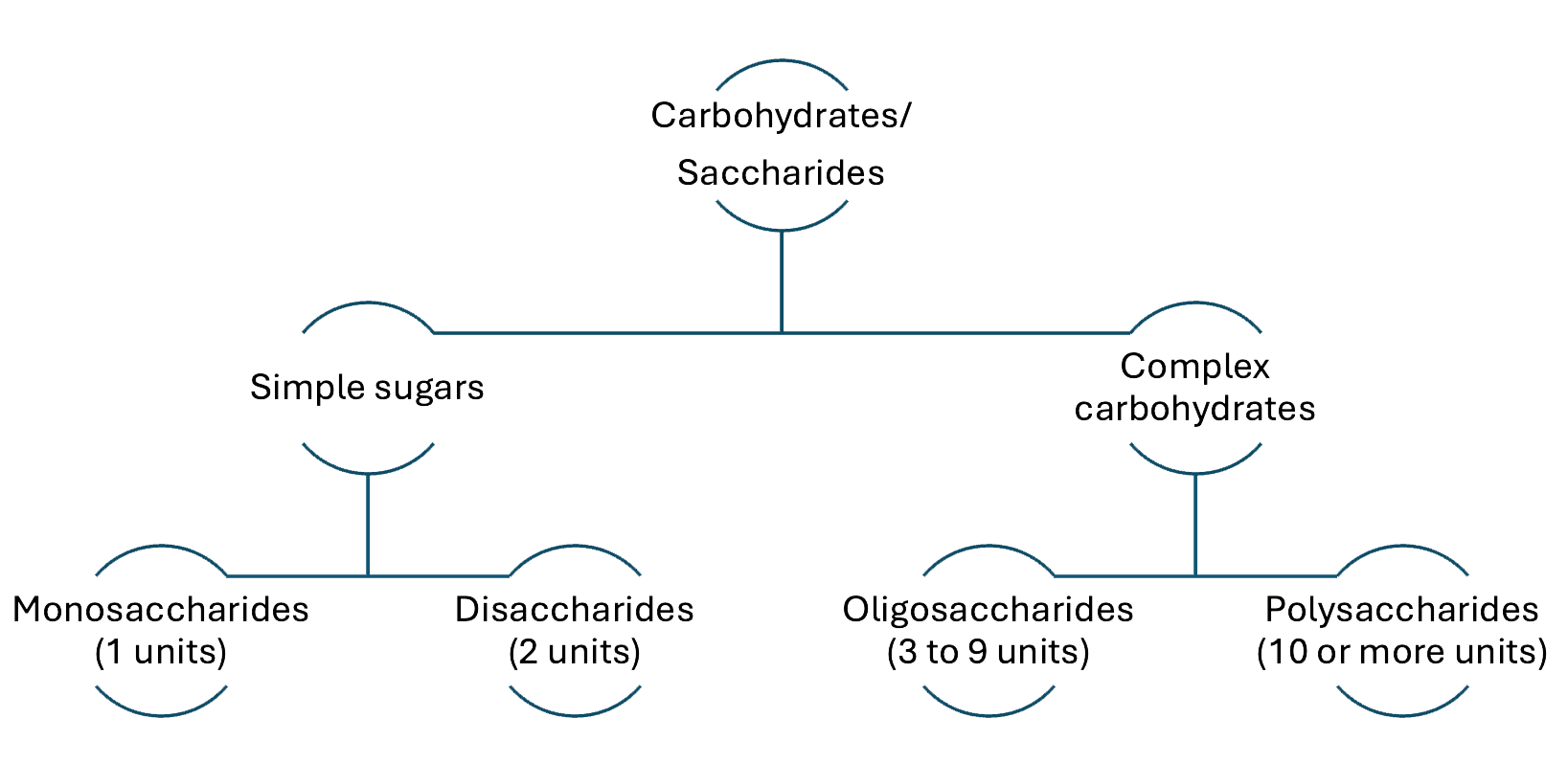
Classification tree of saccharides
The key carbohydrate that the body uses for energy is glucose, a type of monosaccharide. Other carbohydrates, even those that aren’t glucose, need to be converted into glucose or similar compounds for the body to extract meaningful amounts of energy from them. Disaccharides and complex carbohydrates, like starches, must first be broken down into simpler sugars before the body can use them.

Simple representation of the breakdown of an oligo-saccharide into mono-saccharides
Although carbohydrates often receive mixed reviews depending on diet trends, they are an essential part of a balanced diet. Incorporating the right balance of simple and complex carbohydrates helps maintain consistent energy levels and supports overall health. Just as a car needs the right type of fuel to run smoothly, our bodies rely on the right mix of carbohydrates to function at their best.


